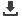
(EN3) Energy consumption within the organization (*)
U.M.
2013
2014
2015
(*)The sum of the indicators differs from the total shown due to rounding up and down of the figures.
Total consumption (*)
Gjoules
18,983,467
17,654,401
18,786,493
- shipboard
18,960,595
17,640,696
18,772,883
- shoreside
22,872
13,705
13,609
Total fleet consumption
TM
469,473
436,340
461,205
- HFO
391,574
344,140
383,967
- LSFO
48,453
59,015
1,750
- MGO
29,446
33,185
75,488
(*) conversion factors applied: fuel 1 TM=40.19 Gj; MGO 1 TM= 43.33 Gj
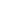
(EN5) Pattern of fleetwide fuel consumption (*)
U.M.
2013
2014
2015
Total shoreside consumption
g/ALB-nm(**)
151.4
149.9
144.96
MT/kALBD(***)
40.9
37.3
35.5
TOE
(Tons of Oil
Equivalent)
1,341.23
1,068.1
1,061.49
- heating
120.05
120.05
120.05
- electricity
1,221.18
948.04
941.44
(*) Data includes all current fleet, excluding from all years any ships transferred out to another brand or sold externally.
(**) ALB-nm stands for Available Lower Berth nautical miles: Available Lower Berth is a standard cruise industry metric of ship passenger capacity and refers to the number of guest beds available on a cruise ship, assuming two people
occupy a cabin. Combining this metric with distance traveled in nautical miles allows the incorporation of guests carried by the fleet as well as the fact that they are transported over distances. Data includes all current fleet, excluding any
ships transferred out to another brand or sold externally.
(***) ALB-km stands for Available Lower Berth kilometers: Available Lower Berth is a standard cruise industry metric of ship passenger capacity and refers to the number of guest beds available on a cruise ship, assuming two people
occupy a cabin. Combining this metric with distance traveled in kilometers allows the incorporation of guests carried by the fleet as well as the fact that they are transported over distances. Data includes all current fleet, excluding any ships
transferred out to another brand or sold externally.
(EN15) Total direct and indirect GHG emissions by weight
U.M.
2013
2014
2015
CO
2
from use of fuel
ton
1,466,597
1,364,139
1,443,357
CO
2
from refrigerant releases
41,775
43,016
31,462
(EN18) GHG emissions intensity
U.M.
2013
2014
2015
kg/ALB-km
0.2548
0.2524
0.2465
(EN20) Emissions of ozone-depleting
substances* CFC-11 equivalent
U.M.
2013
2014
2015
* The ODP (ozone depletion potential) conversion factors are those given in the Montreal
Protocol Technical Papers.
kg
5
1.6
1.17
(EN21) Air Emissions (*)
2013
2014
2015
NOx
ton
30,516
28,362
29,978
SOx
19,770
18,849
18,360
PMs
563
524
554
Significant emissions of NOx
g/ALB-nm
9.8
9.7
9.4
Significant emissions of SOx
6.4
6.5
5.8
Significant emissions of PM
0.182
0.180
0.174
(*)For the calculation of the volume of Sox, NOx and PMs the Company uses conversion factors laid down by Carnival Corporation for the evaluation of ship emissions. There are no GHG emissions standard metrics in the cruise line industry.
With the aim of guaranteeing a system of control and management of the level of impact generated by each ship (from operating the diesel-electric and diesel power plants) the parent company has implemented measures based on existing
International Maritime Organization (IMO) regulations, including the voluntary introduction of a Ship Energy Efficiency Operational Indicator (EEOI) as a monitoring tool for managing passenger ship efficiency performance over time.
(EN8) Water withdrawal/consumption
U.M.
2013
2014
2015
Total water withdrawal by source - shipboard
m
3
3,596,543
3,603,508
3,927,084
- Water supplied
1,051,659
1,407,567
1,252,843
- Water produced
2,602,812
2,295,377
2,763,565
Water consumed per person per day - shipboard (*)
liters
223
220
221
(*) The calculation of the number of people on board per day was carried out by adding the number of passengers on board to the number of crew members (this is a set number for each ship) multiplied by the number of days in the year.
Water consumption in shoreside offices (**)
m
3
8,120
9,937
11,302
(**) including Savona cruise terminal
ENVIRONMENTAL ASPECT
Summary of indicators