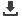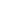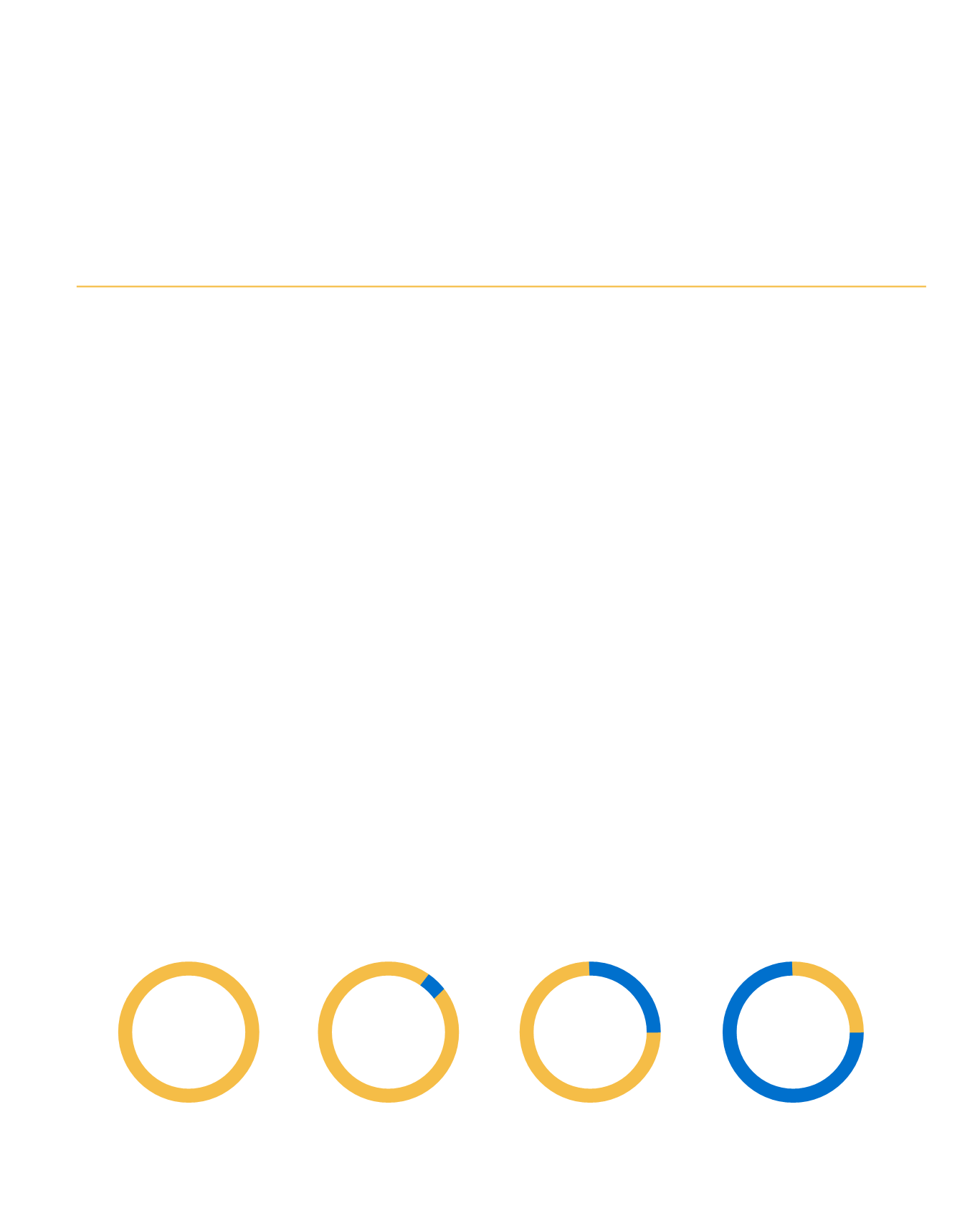
0%
SULFUR DIOXIDE
EMISSIONS
95-
100%
25%
85%
REDUCTION IN
PARTICULATE MATTER
REDUCTION
INNITROGENOXIDES
REDUCTION
IN CARBON EMISSIONS
The 50,000 global ocean-going
commercial vessels are responsible
for a small portion (less than 4%) of
global CO
2
emissions. For perspective,
with roughly 300 cruise ships in the
world, the cruise industry accounts
for just 0.6% of the global maritime
fleet. Cruise ships are a small part of
the overall maritime industry, but
cruise companies have consistently
demonstrated industry leadership
when it comes to implementing
tangible actions tackling the issue of
climate change.
The Carnival Group’s investment in
ships powered by LNG, the world’s
cleanest-known fossil fuel, is a very
important example of responsible
innovation and the pursuit of solutions
enabling the introduction of newer and
more fuel-efficient vessels. Starting in
2018, the Costa Crociere Group will
be the first Company to launch LNG-
powered cruise ships that use gas as
fuel in ports and on the open sea. Liquid
natural gas has been around for decades
but a series of obstacles have until
recently kept it from the cruise industry;
once completed, the transition to LNG-
driven vessels will lead to a considerable
reduction in emissions and demonstrate
to others, in the overall maritime
industry, that LNG is a viable alternative
and, above all, a sustainable choice in
the long term. The vision underlying the
strategic decision to transition to LNG
is based on the need to be a forward
thinking Company. With an average life
cycle lasting several decades, a cruise
ship requires an innovative design that
pre-empts industry trends, guarantees to
exceed environmental compliance and
creates a greener and more sustainable
planet.
LNG: innovation on the way
to a more sustainable future
Benefits of switching from marine diesel to LNG